Urethral Bulking for Stress Urinary Incontinence
In this Health Topic
SUI is a common problem affecting women which is caused by a weakness of the pelvic floor muscles (which help keep the bladder closed), the urethra (the tube through which urine is passed), or the ligaments that support the urethra. This leads to leaking urine with coughing, sneezing, exertion, laughing and other activities which raise the pressure in the abdomen.
Several risk factors are associated with SUI, such as childbirth (1 in 3 women who have had children experience problems with urinary incontinence), obesity, menopause, chronic cough, chronic constipation, or heavy lifting.
Urinary Tract
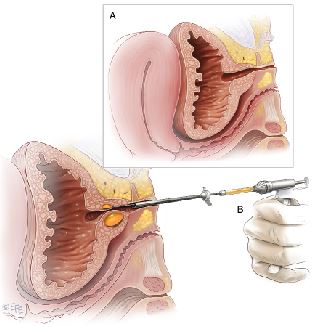
Urethral bulking involves injecting a bulking agent around the urethra. This narrows the urethra, so leakage is less likely to occur. Common bulking agents include collagen (a type of protein found in all our tissues) and water-based gels containing various agents.
- Women who are not fit enough for surgery and anesthesia
- Women who haven’t completed their family
- Women who do not wish to undergo surgery for stress incontinence or for whom conventional surgery has not been fully effective
- Women whose stress incontinence is due mainly to a deficiency in the sphincter muscle surrounding the urethra
Before scheduling you for urethral bulking, your doctor may recommend a urodynamics test. This is an investigation of bladder function, which will confirm your diagnosis and help rule out any other problems with the bladder.
The procedure can be performed under local anesthetic in the clinic or under a general anesthetic in the operating room. Your doctor will discuss which option is best for you. The bulking agent is injected around the urethra just below the neck of the bladder via a cystoscope or specially designed syringe. No incisions, cuts, or stitches in the vagina or abdomen are required for this procedure.
- Anesthetic risks. These will be discussed with you by the anesthetist.
- Bleeding and infection. These are risks of any gynecological surgery. Your doctor may give you a dose of antibiotics prior to the bulking injection. Let your doctor know if you are taking aspirin or blood thinning agents.
- Pain on passing urine. You may notice some initial burning or stinging on passing urine. This will usually settle within 24-48 hours. If you develop urinary frequency, offensive or unusual smelling urine and pain on urination you may have a bladder infection in which case you should call your doctor for advice.
- Difficulty emptying the bladder. Less than 10% of women temporarily have difficulty emptying the bladder completely, requiring a catheter. There are no known long-term risks of difficulty emptying.
- Need for a repeat bulking procedure. A “top-up” of the bulking agent is sometimes needed to optimally control SUI symptoms. The effect of the bulking agent can also sometimes reduce with time, requiring a second injection.
Additional risks can include movement of the bulking material from where it was injected, hypersensitivity/allergy, abscess formation (local infection), or granuloma (a small cyst-like structure where the bulking material was injected). These risks are uncommon, and your doctor will discuss whether they apply to the specific type of bulking agent you will be having.
Most women having bulking agents alone can have the procedure as a day case. Following the bulking procedure your doctor may check to see that you are emptying your bladder adequately using a scanner or a catheter. Some women may have temporary difficulty in passing urine due to swelling from the procedure. In this case, you may be sent home with a catheter which will be removed a few days later once the swelling has settled down. You may also notice some bleeding on passing urine. You may return to normal activities as soon as you feel well enough. If you have had a general anesthetic you should not drive for 24 hours.
60-70% of women undergoing urethral bulking will notice cure or improvement of their SUI symptoms. However, the effect tends to reduce over time, and over a third of women request a second injection. If you have undergone a bulking injection, this will not affect the success rates of any further procedures for stress incontinence that you may undergo in the future.
Overactive bladder (when you get a sudden urgent need to pass urine with or without leaking or passing urine frequently) is caused by a problem with the bladder rather than urethral dysfunction. Thus, bulking agents will not improve this problem. If you have both SUI and overactive bladder symptoms, a bulking agent could be used in combination with a medical or surgical treatment for overactive bladder (e.g. intravesical botox injections or neuromodulation).
Other options for the treatment of stress incontinence include pelvic floor physiotherapy, or surgical options such as mid-urethral slings (a polypropylene tape inserted via a small incision into the vagina to support the urethra), colposuspension (the bladder neck is lifted up using stitches with an open or a key hole abdominal operation), or an artificial urinary sphincter (a major operation involving passing an inflatable cuff around the urethra).
